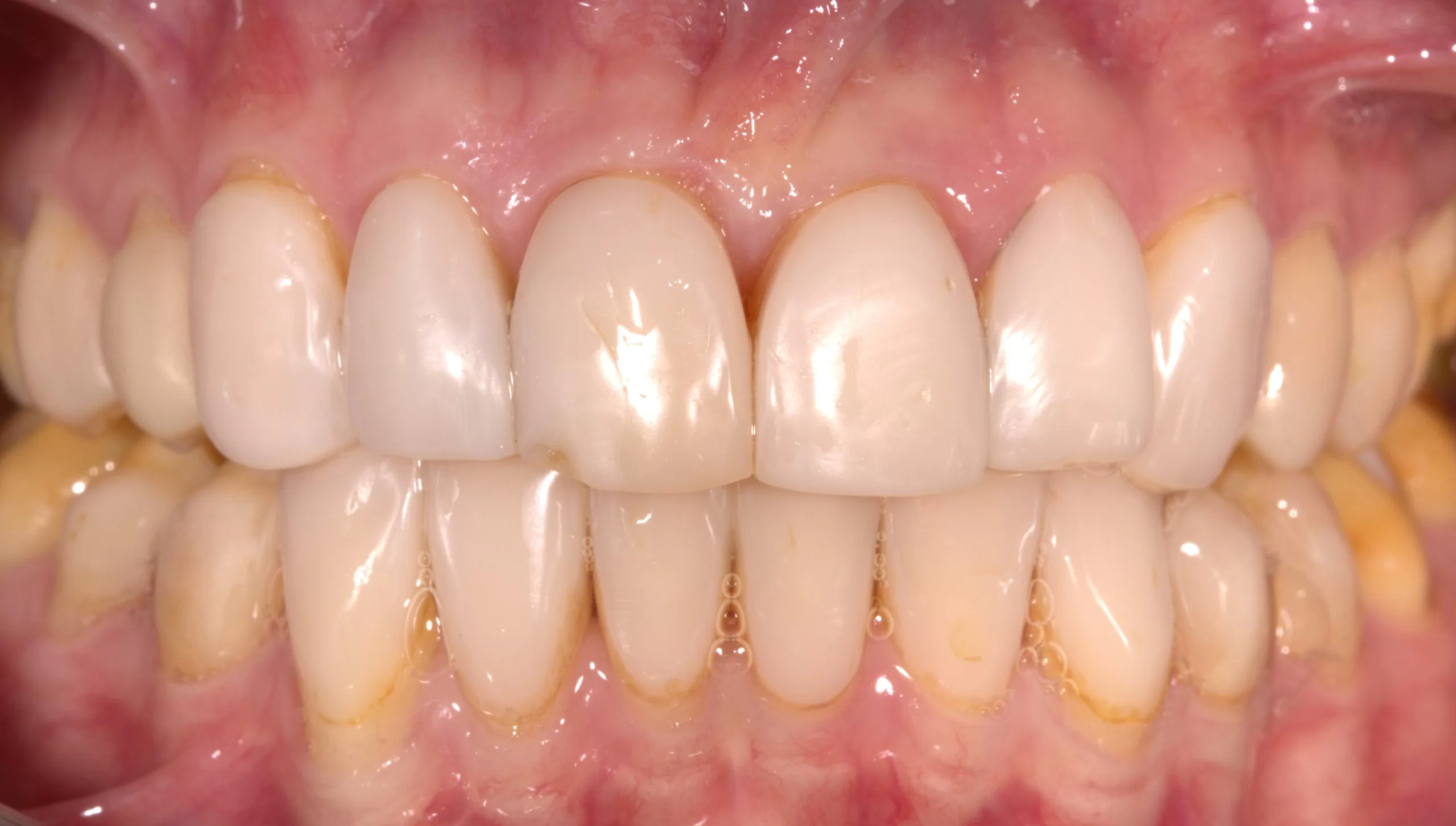
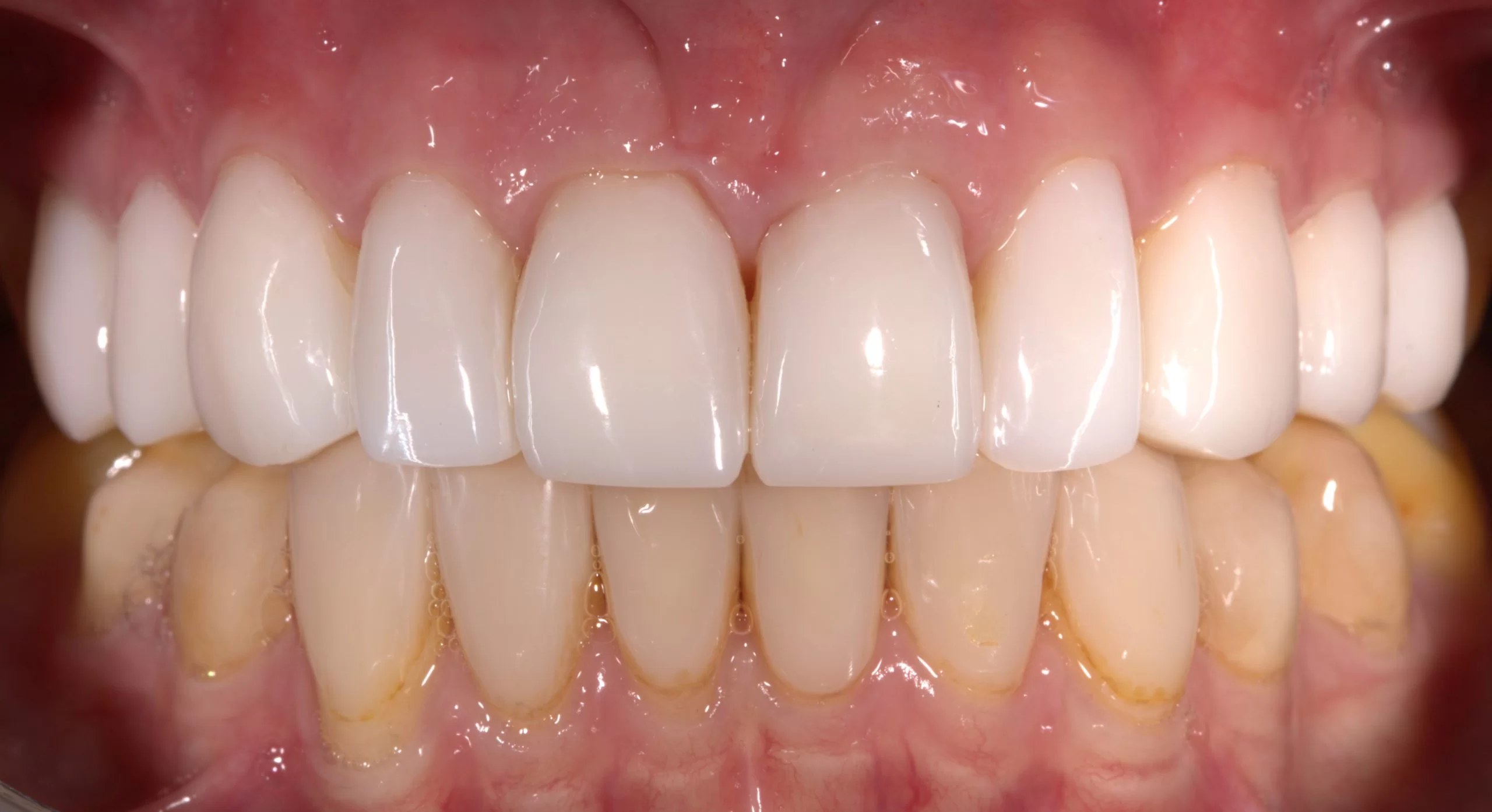
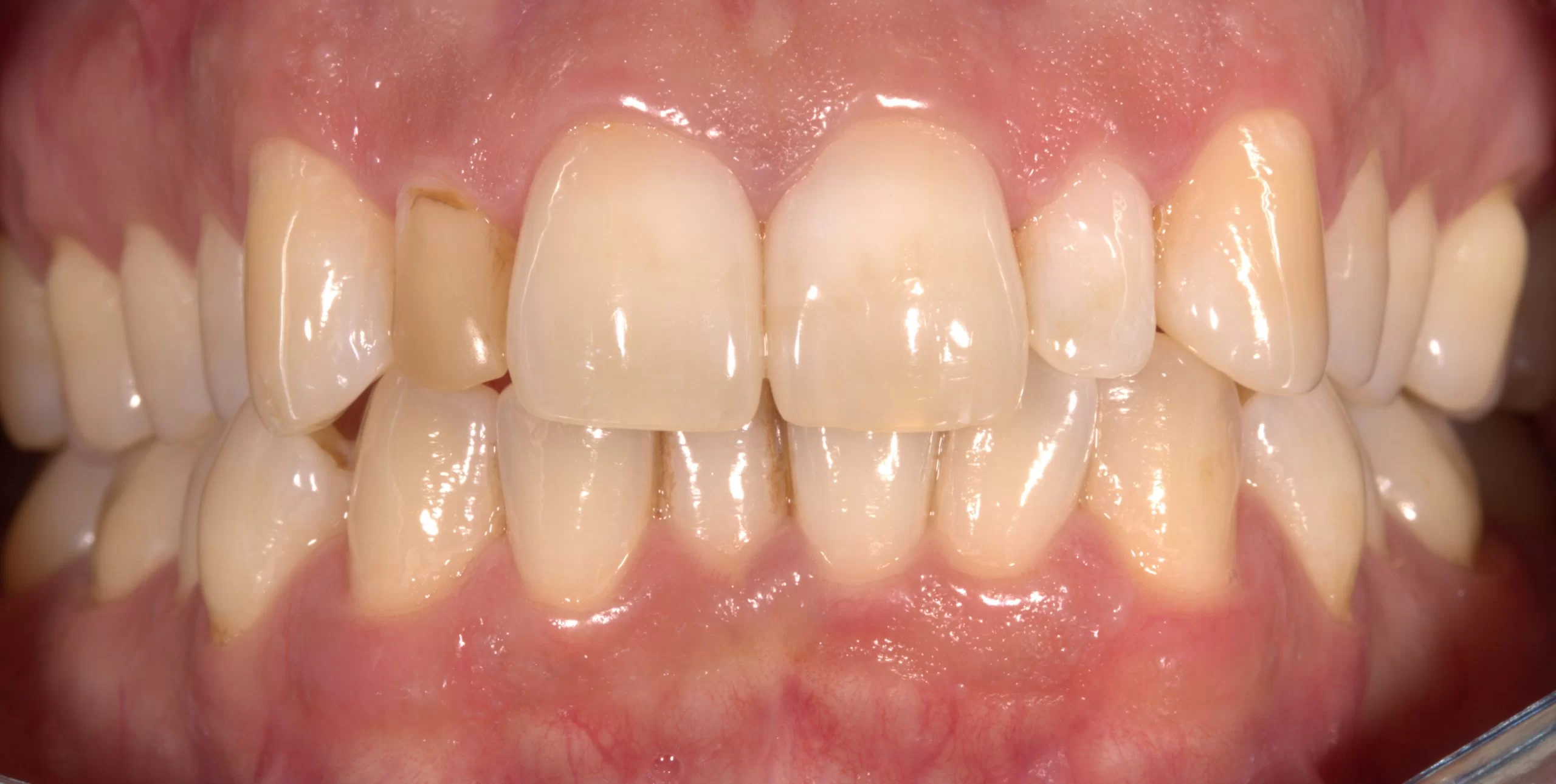
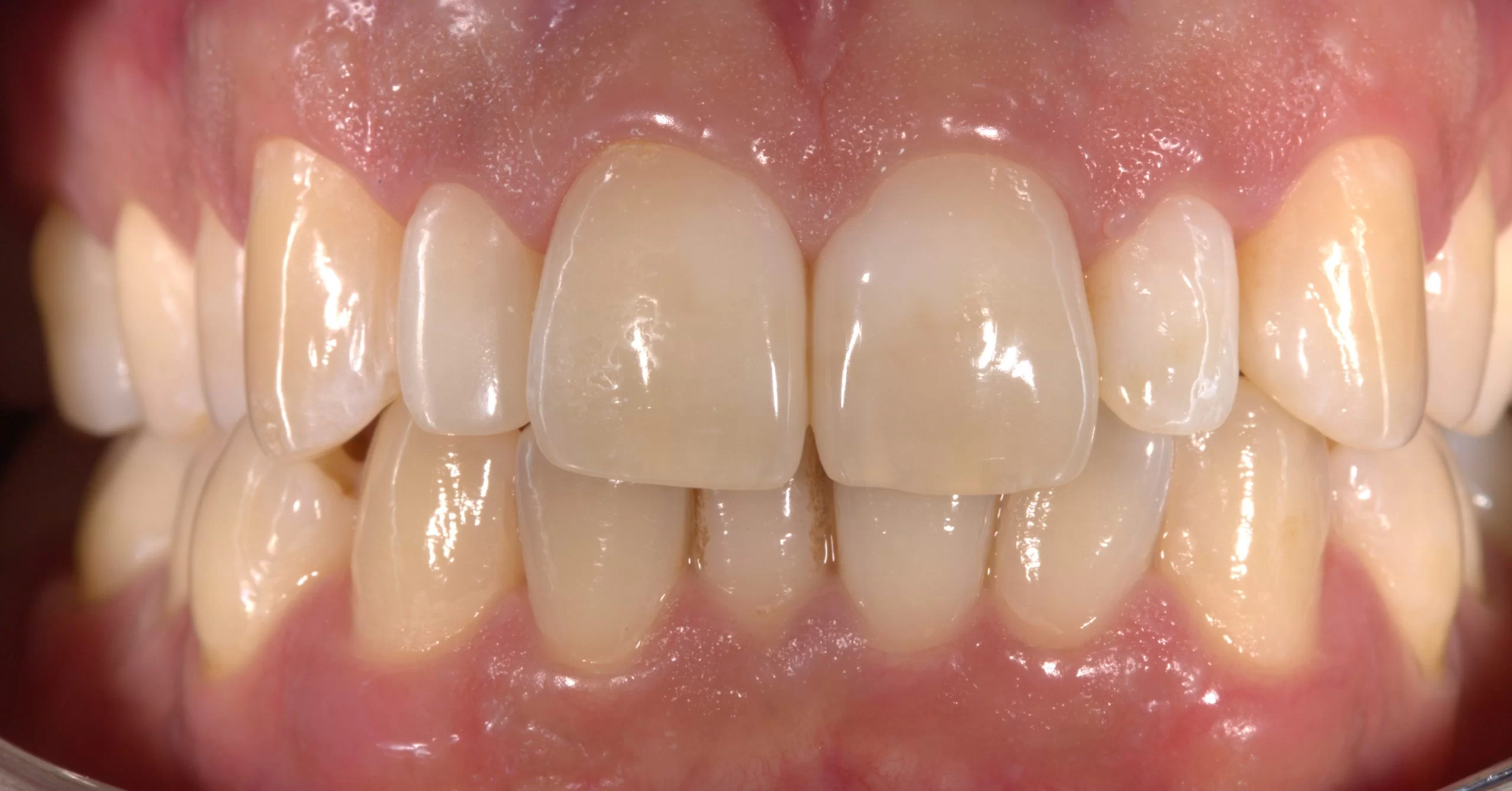
Periodontal disease is the inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. The periodontitis bacteria causes an inflammatory response in the body. The jawbone is affected, causing tooth loss in advanced periodontitis. The dentist not only looks at the health of teeth and molars, but also at the gums. Many people suffer from bleeding gums when brushing. This may mean that the gums are inflamed. The cause of gingivitis is the deposits that settle above and below the gums. This deposit consists of food remains, certain saliva parts and especially bacteria. The acidic secretions of these bacteria cause caries and gingivitis. If this deposit is not removed in time, it will grow in depth towards the tooth root. Space is created between the tooth root and gums, the so-called ‘pocket’. This pocket is the ideal living space for the bacteria.
Be on time
For this reason, it is important to treat periodontal disease as quickly as possible. If periodontal disease is not stopped, it will lead to loosening of the teeth and ultimately tooth loss. Further consequences of untreated periodontal disease can be an increased risk of complications during pregnancy, heart disease and diabetes. Existing periodontitis is stopped by systematic periodontal treatment. The basis of any periodontal treatment is the complete removal of bacterial deposits. The systematic periodontal treatment consists of pre-treatment, main treatment and post-treatment. If necessary, antibiotics are also prescribed.
Aftercare
The disease was first stopped by systematic periodontal treatment. Our daily diet causes deposits to reappear between the teeth and gums. It is therefore important to have the deposits professionally removed at regular intervals (by the dentist or dental hygienist) to effectively prevent recurrence of periodontal disease. The goal is to be able to enjoy a beautiful smile even when you are old, while preserving your own teeth.